Article Plan: Electrical Panel Maintenance Protocol PDF
This document details a systematic approach to electrical panel upkeep, encompassing visual checks, testing, cleaning, and documentation—crucial for safety and reliability.
Electrical panel maintenance is a critical, often overlooked, aspect of facility management. A well-maintained panel ensures consistent, safe power distribution, preventing costly downtime and potential hazards. This protocol outlines a comprehensive approach, moving beyond simple inspections to include detailed testing and preventative measures.
Regular maintenance, documented via a PDF checklist, facilitates a systematic process. This includes verifying secure connections, checking for physical damage, and ensuring proper functionality of circuit breakers. Proactive upkeep extends the lifespan of the panel, minimizes risks, and guarantees compliance with electrical codes and standards. Ignoring these procedures can lead to failures, fires, and significant operational disruptions.
Importance of Regular Electrical Panel Maintenance
Consistent electrical panel maintenance is paramount for operational safety and efficiency. Neglecting upkeep invites risks like overheating, loose connections, and ultimately, electrical failures. Proactive maintenance, guided by a PDF checklist, minimizes these hazards, protecting personnel and equipment.
Regular inspections identify potential issues before they escalate into costly repairs or dangerous situations. Maintaining clean panels—free of dust and debris—improves performance and extends component lifespan. Furthermore, adherence to a maintenance schedule ensures compliance with safety regulations and reduces the likelihood of unexpected downtime, safeguarding productivity and profitability.
Safety Precautions for Electrical Panel Maintenance
Prioritizing safety is non-negotiable during electrical panel maintenance. Strict adherence to Lockout/Tagout procedures is essential – completely de-energizing the panel before any work begins. Qualified personnel must verify zero voltage. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), including insulated gloves, safety glasses, and flame-resistant clothing, is mandatory.
Never work alone, and always inform others of your presence and the task at hand. Maintain a safe working distance from energized parts. Regularly inspect PPE for damage. A detailed PDF protocol should outline these precautions, ensuring all technicians understand and follow them diligently, minimizing the risk of electrical shock or arc flash.
Lockout/Tagout Procedures
Implementing robust Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) procedures is paramount for safety. First, identify all energy sources feeding the electrical panel. Then, properly shut down and isolate each source. Apply individual locks and tags to each disconnecting device, clearly indicating “Do Not Operate.”
Verify the panel is de-energized using a calibrated voltage tester before commencing any work. Only the authorized technician applying the lock can remove it. A comprehensive PDF checklist detailing these steps, including specific lock and tag requirements, is vital for consistent and safe application of LOTO protocols.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Selecting and utilizing appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is non-negotiable when working with electrical panels. This includes wearing electrically insulated gloves with appropriate voltage ratings, safety glasses or face shields to protect against arc flash, and flame-resistant (FR) clothing.
Non-conductive footwear is also essential. A detailed PDF checklist should specify the required PPE based on the assessed risk level of the task. Regular inspection of PPE for damage is crucial, and proper training on its correct use is mandatory for all personnel involved in electrical panel maintenance.
Electrical Panel Maintenance Checklist Overview
A comprehensive electrical panel maintenance checklist, ideally formatted as a PDF for easy distribution and record-keeping, is the cornerstone of a proactive maintenance program. This checklist should encompass visual inspections for damage, verification of proper circuit breaker functionality, and testing of voltage and current loads.
It must also include sections for documenting cleaning activities, checking for corrosion, and confirming panel door security. Utilizing a template.net checklist ensures consistency and thoroughness, promoting safety and minimizing potential downtime. Regular updates are vital.
Visual Inspection Procedures
The initial stage of maintenance involves a detailed visual assessment of the electrical panel. This includes meticulously checking for any physical damage – cracks, rust, or deformation of the enclosure. Inspect the electrical meter for any signs of tampering or malfunction. A crucial step is a panel door security check, ensuring it’s locked to prevent unauthorized access.

Look for signs of overheating, burning, or debris accumulation. Confirm the presence and condition of insulating mats. A general visual inspection forms the foundation for identifying potential issues before they escalate, contributing to a safer and more reliable electrical system.
Checking for Physical Damage
A thorough examination for physical damage is paramount during panel inspection. This begins with scrutinizing the enclosure itself for cracks, dents, or any signs of deformation that could compromise its protective function. Inspect for rust or corrosion, particularly around mounting points and entry points for conduits.
Carefully assess the condition of the panel door and hinges, ensuring secure operation; Look for any evidence of past impacts or attempted forced entry. Document any observed damage, no matter how minor, as it could indicate underlying issues requiring immediate attention and potential repair or replacement.
Inspecting the Electrical Meter
The electrical meter requires careful inspection to ensure accurate energy measurement and identify potential issues. Visually check the meter’s glass cover for cracks or damage, and confirm the display is functioning correctly, showing clear readings. Verify the meter is securely mounted and hasn’t been tampered with.
Record the meter reading as part of the maintenance log. Look for any unusual sounds emanating from the meter, which could indicate internal problems. Ensure the wiring connections to the meter are tight and free from corrosion. Document any discrepancies or concerns immediately for further investigation.
Panel Door Security Check
Maintaining the security of the electrical panel door is paramount for safety and preventing unauthorized access. Verify the door closes securely and the latching mechanism functions correctly. Confirm the door hinges are robust and show no signs of wear or damage. Check if a padlock provision exists and, if so, ensure a suitable lock is in place.
Document the condition of the door and locking mechanism in the maintenance report. A compromised door allows potential hazards and tampering. Ensure the panel door is clearly labeled with appropriate warnings. Any deficiencies must be addressed promptly to maintain a secure electrical environment.
Electrical Connections Inspection
A thorough inspection of electrical connections is vital for preventing failures and ensuring safe operation. This involves verifying the tightness of all screws and terminals within the panel, preventing loose connections that can cause arcing and overheating. Inspect wire integrity for any signs of damage, fraying, or corrosion, replacing compromised wires immediately.
Crucially, confirm each circuit breaker has a secure connection to the busbar. Document any loose connections or damaged wiring in the maintenance report. Proper connections minimize resistance, reduce heat buildup, and maintain system reliability. Regular inspection and tightening are key preventative measures.
Tightness of Screws and Terminals
Ensuring screws and terminals are adequately tightened is a foundational element of electrical panel maintenance. Loose connections create resistance, generating heat and potentially leading to arcing, fires, or equipment failure. Systematically check every screw and terminal within the panel, using a calibrated torque screwdriver to meet manufacturer specifications.
Avoid over-tightening, which can strip threads or damage components. Document any loose or corroded fasteners. Retighten as needed, and replace damaged screws immediately. This simple step significantly reduces the risk of electrical hazards and extends the lifespan of the panel’s components.
Wire Integrity Check

A thorough wire integrity check is paramount for preventing electrical faults. Visually inspect all wiring for signs of damage, including fraying, cracking, or discoloration. Carefully examine insulation for any breaches that could expose conductors. Gently tug on wires at connection points to confirm secure seating – avoid excessive force.
Look for evidence of overheating, such as melted insulation or burned wire. Document any compromised wiring and replace it immediately with appropriately sized conductors. Proper wire integrity ensures reliable current flow and minimizes the risk of short circuits or fires within the electrical panel.
Circuit Breaker Secure Connection Verification
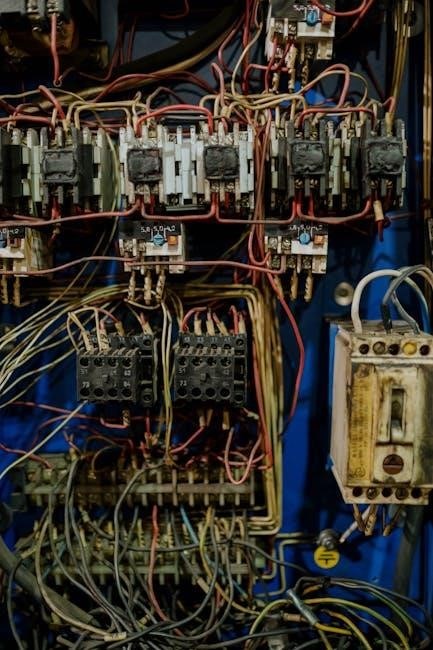
Ensuring circuit breakers are securely connected is vital for reliable protection. Gently but firmly attempt to wiggle each breaker; any movement indicates a loose connection requiring immediate attention. Inspect the breaker’s mounting screws and tighten if necessary, avoiding over-tightening which can damage the panel.
Verify the breaker’s physical condition, looking for cracks or signs of arcing. A secure connection guarantees the breaker will trip correctly during overcurrent events, preventing damage and potential fire hazards. Document any issues and rectify them promptly to maintain panel safety and functionality.
Testing and Measurement Procedures
Accurate testing and measurement are fundamental to proactive panel maintenance. Record voltage measurements at various points within the panel to identify potential imbalances or voltage drops; Simultaneously, measure the current load on each circuit, comparing it to the breaker’s capacity to prevent overloads.
Document all readings meticulously, noting any deviations from expected values. These measurements establish a baseline for future comparisons, enabling early detection of developing issues. Consistent monitoring helps predict potential failures and optimize panel performance, ensuring a safe and efficient electrical system.
Voltage Measurement Recording
Precise voltage measurement recording is a cornerstone of effective panel maintenance. Utilize a calibrated multimeter to measure voltage at the main lugs, feeder circuits, and individual branch circuits. Document each reading, noting the phase-to-ground and phase-to-phase voltages.
Compare recorded values against the panel’s nameplate specifications and expected ranges. Significant deviations may indicate loose connections, transformer issues, or overloaded circuits. Maintain a detailed log of all voltage measurements, facilitating trend analysis and proactive identification of potential electrical problems, ensuring system stability.
Current Load Measurement Recording
Accurate current load measurement is vital for assessing panel capacity and identifying potential overloads. Employ a clamp meter to measure the amperage draw on each circuit while under normal operating conditions. Record these readings alongside the corresponding circuit breaker number and load description.
Compare measured currents to the circuit breaker’s ampacity rating. Exceeding this rating risks nuisance tripping or, more seriously, overheating and fire hazards. Maintain a comprehensive record of current load data, enabling proactive load balancing and preventing system failures, ensuring optimal performance.

Cleaning and Lubrication
Regular cleaning is paramount for maintaining electrical panel efficiency and preventing failures. Use a vacuum cleaner with a brush attachment to remove dust and debris from within the panel, avoiding compressed air which can spread contaminants. Pay close attention to heat sinks and ventilation areas.
For panels containing motors or switchgear, lubricate moving parts according to manufacturer recommendations. This reduces friction, minimizes wear, and ensures smooth operation. Keep a log of lubrication dates and types of lubricant used, contributing to a proactive maintenance schedule and extending equipment lifespan.
Removing Dust and Debris
Dust and debris accumulation significantly impacts electrical panel performance and safety. Utilize a specialized vacuum cleaner equipped with a brush attachment for gentle, yet effective removal. Avoid using compressed air, as it redistributes particles and can introduce moisture. Focus on areas prone to buildup, such as heat sinks, ventilation slots, and the base of the enclosure.
Ensure the panel is de-energized and follow proper lockout/tagout procedures before cleaning. Regularly scheduled cleaning—baked into the maintenance plan—prevents overheating and potential short circuits, contributing to a reliable and safe electrical system.
Lubricating Moving Parts (Motors, Switchgear)
Proper lubrication minimizes friction, reduces wear, and extends the lifespan of moving components within motors and switchgear. Utilize a lubricant specifically designed for electrical equipment, ensuring compatibility with materials and operating temperatures. Apply sparingly, avoiding over-lubrication which attracts dust and debris.

Follow manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and types. Regularly lubricated parts operate more efficiently, reducing energy consumption and preventing premature failure. This proactive step is integral to a comprehensive electrical panel maintenance protocol, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Internal Panel Condition Assessment
A thorough internal assessment is vital for identifying potential hazards and degradation. Inspect for signs of overheating, such as discoloration or burning smells. Ensure the panel interior is clean and free of dust, debris, and any accumulated contaminants.
Critically examine for evidence of moisture or corrosion, which can compromise electrical connections and safety. Look for damaged insulation or loose wiring. A clean, dry, and well-maintained interior significantly reduces the risk of electrical failures and ensures the longevity of the panel. Document any findings meticulously.
Signs of Overheating or Burning
Detecting overheating or burning is paramount for preventing catastrophic failures. Look for discoloration of wires, terminals, or the panel itself – a brownish or blackened hue indicates excessive heat. A distinct burning smell is a critical warning sign, demanding immediate investigation and shutdown.
Inspect for scorched or melted insulation on wires, and examine circuit breakers for signs of damage. Evidence of arcing, like pitting or carbon deposits, also suggests overheating. Promptly address any identified issues to mitigate fire hazards and ensure continued safe operation of the electrical system.
Debris and Contamination Check
Maintaining a clean electrical panel is vital for optimal performance and safety. Regularly inspect for dust, dirt, and other debris accumulation, as these can impede airflow and contribute to overheating. Pay close attention to areas around components like circuit breakers and transformers.
Look for signs of pest intrusion – insects or rodents can cause shorts and damage wiring. Ensure the panel is free from liquids or corrosive substances. Removing contaminants prevents corrosion and ensures reliable electrical connections, extending the lifespan of the panel and minimizing potential hazards.
Moisture and Corrosion Inspection
Moisture is a significant threat to electrical panel integrity, leading to corrosion and potential short circuits. Thoroughly inspect for any signs of water ingress, condensation, or dampness within the enclosure. Check for rust or corrosion on busbars, terminals, and wiring.
Pay particular attention to areas prone to condensation, such as near the bottom of the panel. Corrosion compromises electrical conductivity and can cause equipment failure. Addressing moisture issues promptly prevents further damage and ensures safe operation. Proper ventilation and sealing are crucial for preventing moisture buildup.
Circuit Breaker Functionality Testing
Regularly testing circuit breakers is paramount for ensuring proper operation during overcurrent or short-circuit events. Employ a circuit breaker tester to simulate fault conditions and verify the breaker trips within its specified time and current ratings. Document each test result, noting any discrepancies or failures.
Inspect breakers for physical damage, such as cracks or discoloration. Ensure proper contact pressure and alignment. A malfunctioning breaker can fail to trip, leading to overheating and fire hazards. Testing confirms the protective devices are reliable and safeguards the electrical system.
Backup Power and Safety System Checks
Essential to a comprehensive maintenance protocol are checks of backup power systems, like generators or UPS units. Verify automatic transfer switches (ATS) operate correctly, seamlessly switching to backup power upon utility failure. Test generator start-up and run times under load, ensuring sufficient capacity.
Inspect safety systems, including arc flash protection and grounding mechanisms. Confirm proper functionality of warning labels and emergency shutdown procedures. Regular testing of these systems guarantees continued operation during critical events, minimizing downtime and enhancing safety. Document all test results meticulously for compliance and future reference.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Meticulous documentation is paramount for effective electrical panel maintenance. Maintain detailed records of all inspections, tests, and repairs, including dates, findings, and corrective actions taken. Utilize a standardized checklist (PDF format is ideal) to ensure consistency and completeness.
Record voltage and current measurements, noting any deviations from normal values. Document any observed damage, overheating, or corrosion. These records serve as a historical reference, aiding in trend analysis and proactive maintenance planning. Proper documentation is crucial for compliance with electrical codes and safety regulations.
Frequency of Electrical Panel Maintenance
The frequency of electrical panel maintenance depends on several factors, including the panel’s age, environmental conditions, and load demands. A minimum of annual inspections is generally recommended, but critical systems or harsh environments may require more frequent checks – perhaps quarterly.
Regular visual inspections should be conducted monthly, focusing on obvious signs of damage or overheating. Detailed testing and measurement procedures should be performed annually. Proactive maintenance, guided by a checklist, minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of the electrical system. Consistent scheduling ensures safety and compliance.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical Panel Issues
Common issues include tripped circuit breakers, often indicating overloads or short circuits. Another frequent problem is loose connections, leading to overheating and potential fire hazards. Identifying signs of corrosion or moisture is also crucial, as these can compromise safety.
Overheating or burning smells necessitate immediate investigation. Utilizing a checklist during troubleshooting helps ensure a systematic approach. Regular voltage and load measurements can pinpoint imbalances. Always prioritize safety and, when in doubt, consult a qualified electrician for complex repairs.
Electrical Panel Maintenance Checklist Template (PDF Focus)

A comprehensive PDF checklist is vital for consistent maintenance. It should include sections for visual inspection, noting physical damage, meter readings, and door security. Detailed checks of screw tightness, wire integrity, and breaker connections are essential. Space for recording voltage, current, and any observed anomalies is crucial.
The PDF format allows for easy distribution and digital record-keeping. Template.net offers editable options, streamlining the process; Ensure the checklist covers internal panel conditions, including overheating signs and debris. A completed checklist demonstrates due diligence and compliance.
Utilizing a PDF Checklist for Efficient Maintenance
Employing a PDF checklist streamlines electrical panel maintenance, ensuring no step is overlooked. Digital checklists facilitate easy tracking and documentation, improving accountability. PDFs are readily shareable among maintenance personnel, promoting standardized procedures. Completed forms provide a clear audit trail for compliance purposes.
The format allows for annotations and digital signatures, enhancing record integrity. PDFs can be stored securely and accessed quickly, improving response times. Regular use of a checklist minimizes errors and promotes proactive maintenance, ultimately reducing downtime and costs.

Advanced Diagnostic Tools for Electrical Panels
Beyond standard testing, advanced tools elevate panel diagnostics. Infrared thermography detects overheating components, preventing failures before they occur. Ultrasonic detectors identify arcing and corona discharge, pinpointing hidden issues. Power quality analyzers assess voltage fluctuations and harmonic distortion, ensuring optimal performance.
Circuit tracer tools aid in identifying wiring faults, reducing troubleshooting time. Digital multimeters with advanced features provide precise measurements. These tools, combined with skilled technicians, enable proactive maintenance and minimize downtime, enhancing safety and reliability of the electrical system.
Compliance with Electrical Codes and Standards
Adhering to electrical codes is paramount for safety and legal compliance. National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines dictate panel maintenance practices, ensuring installations meet minimum standards. Local regulations may impose additional requirements, necessitating thorough understanding.
Regular inspections must verify compliance with these codes, documenting findings meticulously. Maintaining records demonstrates due diligence, protecting against liability. Qualified electricians must perform maintenance, possessing up-to-date knowledge of relevant standards. Compliance safeguards personnel, property, and ensures the electrical system operates reliably and safely.
Training Requirements for Electrical Panel Maintenance Personnel
Comprehensive training is essential for personnel performing electrical panel maintenance. Qualified individuals require instruction in safety protocols, including Lockout/Tagout procedures and PPE usage. Training should cover NEC guidelines, relevant electrical codes, and troubleshooting techniques.
Competency assessments verify understanding and practical skills, ensuring safe and effective maintenance practices. Regular refresher courses keep personnel updated on evolving standards and technologies. Certification programs demonstrate commitment to professional development and adherence to industry best practices, minimizing risks and maximizing system reliability.
Cost Benefits of Proactive Electrical Panel Maintenance
Proactive electrical panel maintenance delivers significant cost savings. Preventing failures reduces expensive emergency repairs and downtime, boosting operational efficiency. Regular inspections identify and address minor issues before they escalate into major problems, extending equipment lifespan.
Optimized energy consumption lowers utility bills, while improved safety minimizes the risk of costly accidents and insurance claims. A well-maintained panel enhances system reliability, protecting valuable equipment and data. Investing in preventative maintenance offers a substantial return, ensuring long-term cost-effectiveness.
Environmental Controls within Electrical Panels
Maintaining optimal environmental conditions inside electrical panels is crucial for reliability. Controlling temperature and humidity prevents corrosion and component degradation. Regularly check for moisture and debris accumulation, as these can lead to short circuits and failures.
Ensure adequate ventilation to dissipate heat generated by electrical components, extending their lifespan. Proper sealing prevents dust, dirt, and pests from entering the panel, maintaining clean operation. Monitoring these factors proactively minimizes risks and ensures consistent performance, safeguarding the entire electrical system.
Power Supply and Internal Components Inspection
A thorough inspection of the power supply and internal components is paramount for panel health. Verify voltage levels are within acceptable ranges and check for any signs of overheating or damage to transformers and power distribution units. Inspect wiring for insulation integrity, loose connections, and corrosion.
Examine capacitors for bulging or leakage, and assess the condition of fuses and relays. Ensure all components are securely mounted and free from debris. Regularly checking these elements proactively identifies potential issues, preventing unexpected downtime and ensuring a stable power supply.
Control System Components Maintenance

Maintaining control system components within the electrical panel is vital for operational efficiency. Inspect Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), Human Machine Interfaces (HMIs), and other control devices for proper functionality and communication. Check wiring connections and ensure secure mounting to prevent signal interference.
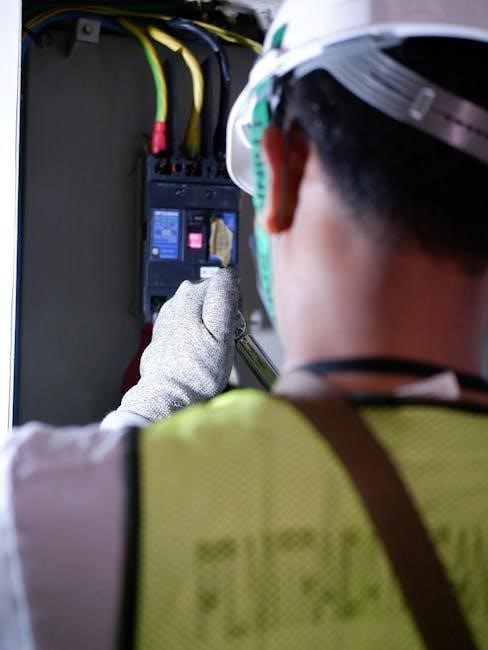

Regularly test input/output modules and verify the accuracy of sensors and actuators. Lubricate moving parts as needed and clean components to remove dust and debris. Proactive maintenance of these systems minimizes downtime, enhances system reliability, and ensures precise control over electrical processes.




